Diabetes Causes, Diabetic care routine, and Cure Tips are here to prevent it from us. Diabetes is a chronic condition that has a significant impact on human life. With its prevalence on the rise globally, understanding the effects of diabetes is crucial for individuals, communities, and healthcare systems. Diabetes Is due to an unhealthy lifestyle.
Diabetes also places a substantial economic burden on individuals and healthcare systems. Diabetes Causes, Diabetic care routine, and Cure Tips are here to prevent it from us. Diabetes is a chronic condition that has a significant impact on human life. With its prevalence on the rise globally, understanding the effects of diabetes is crucial for individuals, communities, and healthcare systems. Diabetes Causes are due to an unhealthy lifestyle.
How does diabetes cause to arise?
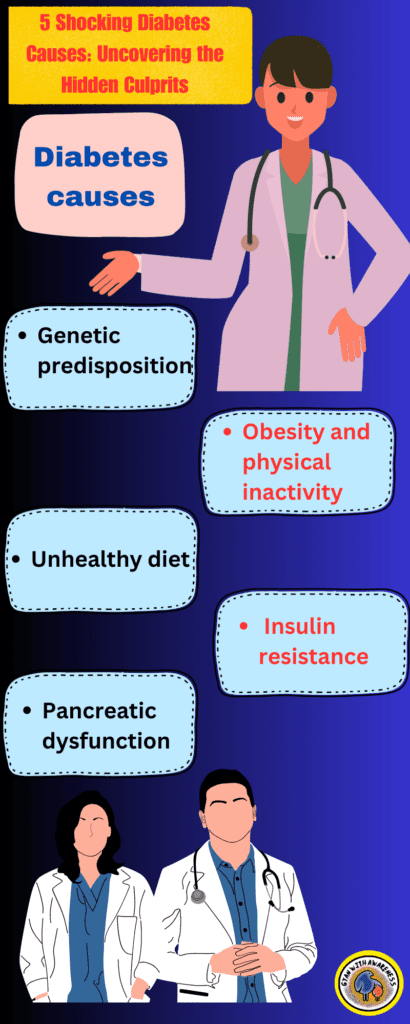
The development of diabetes is influenced by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Here are five key factors that contribute to the development of diabetes or the reason behind diabetes causes.
👉2. Obesity and physical inactivity:
👉3. Unhealthy diet:
👉4. Insulin resistance:
👉5. Pancreatic dysfunction:
It is important to note that, while these (diabetes causes ) characteristics may increase the probability of acquiring diabetes, not all individuals who exhibit these risk aspects will develop the disease. Activity regularly, a healthy weight, and a nutritious diet all contribute to lowering the risk of acquiring diabetes while also managing it efficiently.
Read More: Best 7 Diabetic Foot Care And Cure Tips
Although diabetes is incurable, it can be effectively managed through an everyday schedule that includes:
👍1. Eating a nutritious and wholesome diet rich in genuine fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
👍3. Taking the drugs prescribed and continually tracking blood sugar levels as directed by a healthcare professional.
👍4. Using portion control and mindful eating to control carbohydrate intake and keep blood sugar levels stable.
👍5. Stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and participation in hobbies.
👍6. Getting sufficient sleep to support overall health and hormone regulation.
👍7. Maintaining regular check-ups with healthcare professionals for monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan.
👍8. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, diabetes educators, or support groups for guidance and motivation.
👍9. Staying informed about diabetes management strategies and advances in treatment options.
👍10. Making lifestyle changes for the long term and adopting healthy habits as part of a sustainable approach to diabetes management.
It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized plan and make necessary adjustments based on personal needs and medical advice.
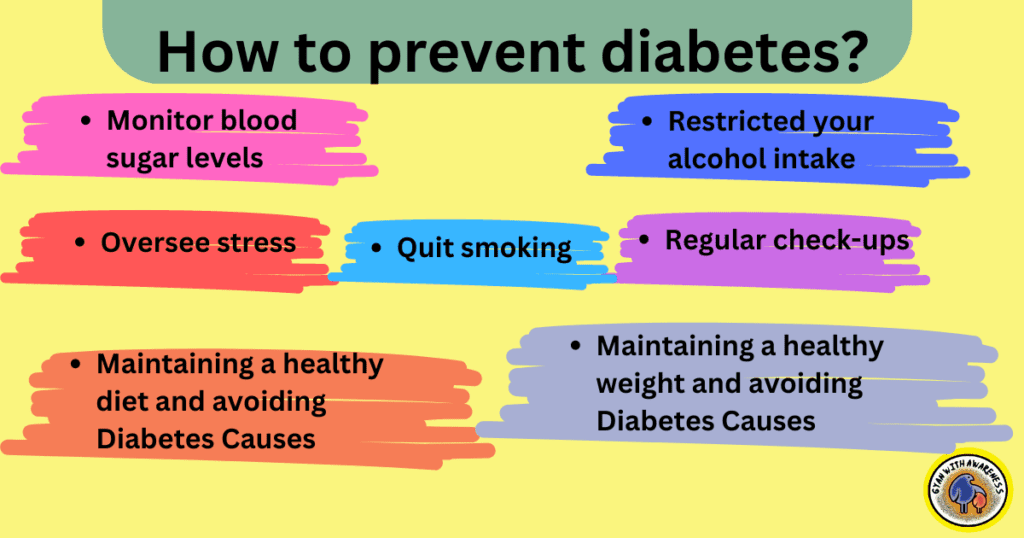
How to prevent diabetes?
To manage and prevent diabetes, here are some effective strategies:
📌1. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding Diabetes Causes
Going without unwanted pounds and maintaining a healthy body weight may boost the sensitivity to insulin and help control blood glucose levels. Consistent physical activity and a nutritious diet are essential components of maintaining a healthy weight.
📌2. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding Diabetes Causes
Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises (such as walking, jogging, or cycling) and strength training exercises.
📌3. Monitor blood sugar levels:
Regularly check and monitor your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider. This helps in understanding how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications.
📌4. Oversee stress:
Prolonged stress can have an impact on your glucose levels and overall health. Find healthy ways to cope with it, such as performing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from friends and family.
📌5. Restricted your alcohol intake:
Excessive consumption of alcohol can disrupt your glucose levels and contribute to weight gain. If you must consume alcohol, do so in moderation and always with food.
📌6. Quit smoking:
Being a smoker raises the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems. Quitting smoking improves overall health and lowers the risk of diabetes complications.
📌7. Regular check-ups:
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor the state of your blood sugar, manage any existing conditions, and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Individuals can use these strategies to effectively manage diabetes, avoid complications, and live a healthier life. It is critical to collaborate closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized plan based on specific needs and health issues.
💡FAQ
🔍What are the common early symptoms of diabetes?
👉The common early symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet. These symptoms may vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any noticeable signs. If you have concerns about your health or are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early detection and management of diabetes can help prevent complications and promote better overall health.
🔍What are the sensations or feelings that occur when diabetes develops?
👉 Increased thirst: Constant thirst and an unquenchable thirst for fluids.
👉Frequent urination: Urinating more frequently, including at night (nocturia), as a result of the kidneys working harder to eliminate excess sugar.
👉Fatigue: Excessive tiredness and lack of energy, even after adequate rest.
👉Unintentional weight loss: Losing weight despite having a normal or increased appetite.
👉Blurred or fluctuating vision as a result of high blood sugar levels affecting the fluid balance in the eyes.
👉Slow healing: Wounds, cuts, or sores heal more slowly than usual.
👉Tingling or numbness: Tingling or numbness sensations, particularly in the hands, feet, or legs, which may indicate nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy).