The tips and recommendations offered in this guide empower individuals with diabetes to actively participate in their healthcare journey and make positive changes to promote better health outcomes. Whether you are newly diagnosed with diabetes or have been managing the condition for years, this guide serves as a valuable resource to support your overall health and disease management efforts.
Diabetes and Other-complications:
Common Complications Due to Diabetes:
Cardiovascular complications:
Diabetes greatly increases the likelihood of developing heart-related conditions like coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure, and stroke.
Kidney complications:
It serves as the primary contributor to the onset of chronic kidney disease. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can lead to vein damage, and in more severe instances, it may even result in kidney failure, necessitating treatments such as chemotherapy or surgical intervention.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy):
Diabetes carries the risk of nerve damage, referred to as diabetic neuropathy, which can impact nerves throughout the entire body. This condition can present symptoms like numbness, tingling, pain, or weakness in the extremities. It has the potential to affect different regions, including the feet, legs, hands, and internal organs.
Eye Complications (Retinopathy):
Foot complications:
Diabetes can also result in foot problems due to nerve damage and poor blood circulation in the feet. This increases the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and serious complications like gangrene. Maintaining proper foot care and attending regular check-ups are essential to prevent these complications.
Skin complications:
Diabetes makes people more prone to a variety of skin disorders. Elevated blood sugar levels can cause dry skin, slowed wound healing, and increased susceptibility to skin infections. Fungal infections, bacterial infections, and itching are all frequent skin disorders associated with diabetes.
Mental Health Disorders:
Diabetes can impact mental health and increase the risk of conditions such as depression and anxiety. The burden of managing diabetes, the impact on daily life, and the worry about complications can contribute to emotional distress. Proper support and counseling are essential for managing mental health alongside diabetes.
Dental complications:
Diabetes can have an impact on oral health, increasing the likelihood of gum disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss. High blood sugar levels create an excellent environment in the mouth for germs to thrive, leading to oral health concerns.
Complications of gestational diabetes:
Gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that occurs only during pregnancy, can cause several complications that must be carefully monitored. The following are the key points that summarize these complications:
High Blood Sugar Levels: Gestational diabetes causes elevated insulin levels, which can harm both the mother and the developing baby.
Macrosomia: Babies born to mothers who have uncontrolled gestational diabetes are at risk of being larger than average, increasing the likelihood of birth complications.
Hypoglycemia: Following birth, these babies may experience low blood sugar levels, necessitating medical intervention.
Preterm Birth: Gestational diabetes can raise the risk of preterm labor and delivery, necessitating specialized care for the premature baby.
Preeclampsia: Mothers with gestational diabetes might have an increased risk of developing high blood pressure and preeclampsia, a serious condition that can harm both mother and baby.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk: Women who experience gestational diabetes are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
Childhood Obesity: Babies exposed to gestational diabetes are more likely to develop obesity and type 2 diabetes in childhood and adulthood.
Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Babies born to mothers who have poorly controlled gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing respiratory distress syndrome shortly after birth.
Increased Monitoring: Pregnant women with gestational diabetes require more frequent medical check-ups, glucose monitoring, and dietary adjustments to effectively manage their condition.
Understanding the potential complications of gestational diabetes highlights the importance of early detection, consistent monitoring, and proactive management to ensure the mother’s and unborn child’s well-being.
It is crucial to acknowledge that not all people with diabetes will experience these conditions. Nevertheless, the likelihood of developing them is considerably higher compared to those without diabetes. By adopting lifestyle changes, taking prescribed medications, and undergoing regular medical examinations, individuals can effectively manage their diabetes, reducing the risk and severity of these complications. Close collaboration with healthcare providers is essential for monitoring and addressing potential health concerns in individuals with diabetes.

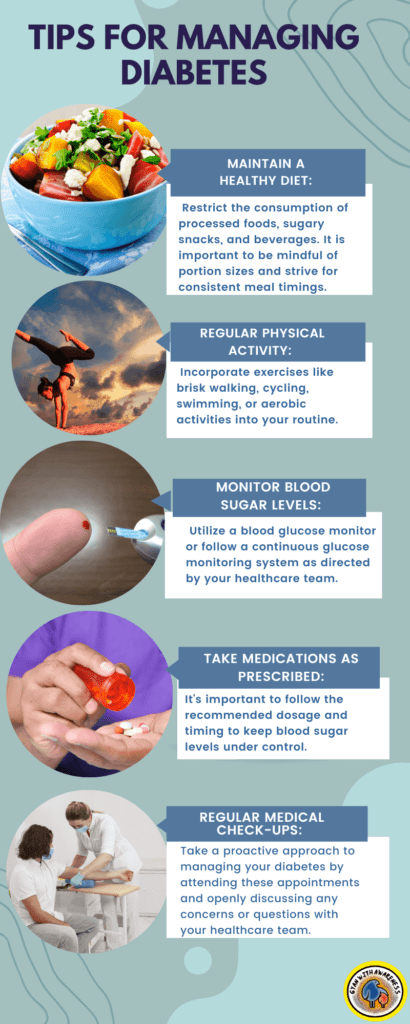
Tips to Manage Diabetes:
Maintain a Healthy Diet:
Regular Physical Activity:
Engage in regular physical activity to help control blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises twice a week.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
Take Medications as Prescribed:
If prescribed by your healthcare provider, take diabetes medications as directed. This may include oral medications or insulin injections. Consult your healthcare provider if you experience any side effects or have concerns about your medications.
Regular Medical Check-ups:
In conclusion, “Powering Through Complications: Decoding 8 Health Risks Linked to Diabetes” offers a transformative perspective on navigating the challenges of diabetes-related complications. By unraveling the intricate web of potential health risks, this guide empowers individuals to take charge of their well-being. Through informed decision-making and proactive measures, readers can mitigate the impact of diabetes on their lives. Emphasizing the importance of education and awareness, the guide underscores that facing complications head-on is not only achievable but also essential for maintaining a high quality of life.
By arming readers with knowledge and strategies, this resource equips them to tackle the complexities of diabetes with resilience and determination. With each insight, the journey becomes less daunting, and the path to better health becomes clearer—a testament to the power of knowledge and the human spirit’s capacity to conquer adversity.
FAQ:
What other diseases come with diabetes?
Diabetes often brings along a range of related health conditions. These can include cardiovascular issues like heart disease and high blood pressure. Nerve damage, known as neuropathy, and kidney problems may also arise. Additionally, diabetes is linked to eye complications such as diabetic retinopathy, and it can weaken the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections. Maintaining proper glucose control and adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial to minimizing the risk of these coexisting health challenges.
Who suffers from diabetes?
People of various ages and backgrounds can suffer from diabetes. While it’s commonly associated with adults, it’s increasingly affecting children and adolescents due to lifestyle factors. Those with a family history of diabetes, obesity, or inactive lifestyles are at higher risk. Additionally, certain ethnic groups, like African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, are more susceptible. The prevalence also rises with age. Vigilant monitoring, healthy habits, and regular medical check-ups are vital for everyone, especially those at higher risk, to manage or prevent diabetes.
What is the main reason for diabetes?
Diabetes is caused primarily by the body’s inability to regulate its glucose levels properly. By accident, the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. In the body, resistance to glucose develops. Diabetes is aggravated by lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of physical activity. Diabetes susceptibility is also increased by a family history of the disease.
What are the 10 warning signs of diabetes?
The warning signs of diabetes encompass various symptoms. These include excessive thirst and hunger, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing cuts or bruises, tingling or numbness in hands and feet, recurrent infections, and dark patches on the skin. Persistent high blood sugar levels lead to these symptoms. Recognizing these signs is vital for early diagnosis and prompt management. If experiencing multiple symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended to assess the possibility of diabetes and initiate appropriate interventions.
What is the normal sugar level by age?
Normal glucose levels in the blood can vary depending on age. Fasting in adults typically ranges from 70 to 100 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.6 mmol/L). However, these levels can vary slightly in older adults. Fasting levels in children and adolescents are typically lower, ranging from 70 to 90 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.0 mmol/L). It should be noted that these values may vary depending on individual circumstances and medical guidelines. Regular monitoring, a healthy lifestyle, and consultation with a healthcare provider all contribute to optimal levels of glucose in people of all ages.
