In this guide, “7-Day High Blood Pressure Diet Menu: Optimize Your Heart Health”, we will delve into ten valuable tips for creating a High Blood Pressure Diet Menu, that supports individuals in their journey toward better blood pressure management. These tips encompass a diverse range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and heart-healthy fats. Additionally, we’ll explore smart cooking techniques, mindful eating practices, and the importance of staying hydrated.
The health problem of hypertension, also referred to as high blood pressure, affects millions of people all over the world. Adopting a heart-healthy diet is just as crucial to controlling it as using medicine, which can be very helpful. A balanced diet can improve cardiovascular health overall, minimize the likelihood of issues, and assist control of blood pressure. So here High Blood Pressure Diet Menu will provide perfect guidelines for you.

A menu for a high blood pressure diet or High Blood Pressure Diet Menu must carefully examine nutrient-rich meals, portion sizes, and limiting sodium intake. This menu encourages a comprehensive strategy for healthy living in addition to focusing on lowering blood pressure.
By following these recommendations and incorporating them into your daily routine, you’ll not only be taking proactive steps to lower high blood pressure, but you’ll also be fostering an environment that encourages overall health and well-being. Always keep in mind that a heart-healthy diet entails more than just what you eat; it also entails adopting a varied, nutrient-rich menu that nourishes your body and promotes a lively, active lifestyle.
Also Read: The Benefits of Tofu: Best Diabetes-Friendly Food, Part 12
Diabetes Cure | Best Mediterranean Chickpea Salad | Part 11
Innovative Grilled Salmon Recipes | Diabetes Cure | Part 10
Diabetes Cure | Delicious Barley Vegetable Soup | Part 9
Delicious Gooseberry Chutney | Diabetes Cure | Part 8
Exquisite Lentil Salad | Diabetes Cure Recipes | Part 7
Best Diabetes Cure | Grilled Fish Recipes | Part 6
Best Diabetes Cure | Brazil Nuts Recipes | Part 5
Best Diabetes Cure | Greek Yogurt Smoothie Recipes | Part 4
Best Diabetes Cure | Greek Salad Recipe | Part 3
Powerful Diabetes Cure Recipes | Detox Island Green Smoothie | Part 2
Best Diabetes Cure | Curd Rice Recipe | Part 1
Factors Leading to High Blood Pressure–
Dietary Patterns: Blood pressure can be increased by eating a diet high in sodium, saturated fats, and processed foods.
Body Weight: Being obese or overweight puts more strain on the heart and blood vessels, which raises the risk of hypertension.
Inactivity: Living a sedentary lifestyle can cause weight gain and, as a result, high blood pressure.
Use of tobacco products: Smoking and using tobacco products can raise blood pressure momentarily and harm blood vessels.
Heavy drinking: Heavy drinking has been linked to hypertension and can also result in other heart-related issues.
Stress: Long-term stress can raise blood pressure by inducing the “fight-or-flight” response in the body, which raises both heart rate and blood pressure.
Genetic Predisposition: An individual’s vulnerability to hypertension may be increased by a family history of the ailment.
Growing Older: As people age, their blood pressure tends to increase, leaving them more prone to hypertension.
Medical Conditions: Certain health conditions, such as kidney disease, diabetes, and sleep apnea, can elevate blood pressure.
Medications: Some medications, including certain birth control pills, decongestants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can cause or exacerbate high blood pressure.
Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause can influence blood pressure regulation.
Excessive Sodium Intake: A diet high in salt can lead to fluid retention, thereby increasing blood pressure.
Chronic Ailments: Conditions like high cholesterol and insulin resistance can contribute to hypertension.
Understanding these factors empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices and work closely with healthcare providers to effectively manage and prevent high blood pressure.
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu:
A high-blood pressure diet menu is a carefully selected meal plan that is intended to help people control and manage their blood pressure levels. High Blood Pressure Diet Menu, emphasizes nutrient-rich, heart-healthy meals while lowering sodium intake, which is crucial for managing hypertension. Lean proteins, healthy fats, a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and whole grains are often included in this menu. High Blood Pressure Diet Menu, tries to deliver vital nutrients including fibre, calcium, magnesium, potassium, and all of the other components that support cardiovascular health.
Furthermore, a High Blood Pressure Diet Menu encourages portion control to maintain a healthy weight, which is instrumental in blood pressure management. It also advises against excessive consumption of processed and high-sodium foods, which can contribute to elevated blood pressure levels.
By following a High Blood Pressure Diet Menu, individuals can take proactive steps toward preventing complications associated with hypertension. It serves as a valuable tool in supporting overall cardiovascular well-being and is often recommended as part of a comprehensive approach to health and wellness.
Why High Blood Pressure Diet Menu Important:
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu holds paramount importance in managing hypertension and safeguarding overall cardiovascular health. Here’s why it is crucial:
Regulation of Sodium Intake: Excessive sodium consumption is a primary contributor to high blood pressure. A well-crafted diet menu emphasizes low-sodium options, reducing the strain on the heart and blood vessels.
Nutrient-Dense Foods: A balanced menu focuses on incorporating nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants vital for heart health.
Balanced Nutrient Ratios: The menu promotes an optimal balance of nutrients, including potassium, calcium, magnesium, and fiber, which play pivotal roles in blood pressure regulation and overall cardiovascular function.
Weight Management: A high blood pressure diet menu encourages portion control and limits excessive calorie intake. This aids in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related hypertension.
Reduction of LDL Cholesterol: A heart-healthy diet can help lower “bad” LDL cholesterol levels, a crucial factor in preventing plaque buildup in arteries, and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
Lowering Triglycerides: This type of diet can lead to lower triglyceride levels, further supporting heart health and reducing the risk of complications.
Improved Blood Sugar Control: A high blood pressure diet menu can also positively impact blood sugar levels, benefiting individuals with hypertension who may also have diabetes or insulin resistance.
Long-Term Health Benefits: Following a high blood pressure diet menu can result in sustained reductions in blood pressure, providing long-term defense against issues caused by hypertension.
Increased Comprehensive Cardiac Health: By addressing key dietary components, this menu helps to create an environment that is favorable for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and lowering the risk of stroke, coronary artery disease, and other related disorders.
Ways to Lower Blood Pressure:
For general heart wellness, lowering excessive blood pressure is essential. Applying these lifestyle adjustments and techniques can successfully control and lower blood pressure levels:
Adapt a heart-healthy diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and low-fat dairy products. Limit sodium intake and abstain from overindulging in processed meals.
Regular Exercise: Exercise regularly for at least 30 minutes a day, seven days a week, by running, brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
Weight management: Using a balanced diet and regular exercise, reach and maintain a healthy weight. Blood pressure can be markedly reduced by losing extra weight.
Limit Your Alcohol Consumption: If you do drink, do so sparingly. This normally means up to two drinks for males and up to one for women per day.
Tobacco usage elevates blood pressure and increases the risk of heart disease; therefore, you should stop smoking. To stop smoking, look for resources and help.
Practice stress-relieving exercises like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to lower your stress levels.
Limit Your Caffeine Intake: Although Moderate Caffeine Intake Is Generally Safe, Excessive Intake May Increase Blood Pressure.
Monitor Blood Pressure: Regularly measure your blood pressure at home using a reliable monitor. Keep a log to track changes over time.
Medication Adherence: If prescribed, take medication as directed by your healthcare provider. Follow up with them regularly for adjustments if needed.
Reduce Processed Foods: Minimize consumption of packaged, processed, and fast foods. These often contain high levels of sodium and unhealthy fats.
Increase Potassium Intake: Incorporate potassium-rich foods like bananas, oranges, spinach, and sweet potatoes into your diet, as potassium helps counteract the effects of sodium.
Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of good sleep each night, as insufficient sleep can lead to high blood pressure.
Seek Professional Advice: Create a specialized plan for controlling high blood pressure in conjunction with your healthcare practitioner.
Top Foods for Managing High Blood Pressure:
A nutritious, well-balanced diet is necessary for managing high blood pressure. To help control its levels, incorporate the heart-healthy foods recommended below into your meals:
Swiss chard, kale, spinach, collard greens, and spinach are high in potassium, a mineral that helps regulate salt levels and decrease blood pressure.
Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are loaded with flavonoids, which have been related to lowering blood pressure.
The body converts the nitrates in beets into nitric oxide, which enhances blood flow and vasodilation.
Oats are abundant in fibre and help to manage blood pressure and decrease cholesterol.
Fruits high in potassium, like bananas, are great for preserving normal blood pressure.
Fish: Omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health and may help decrease blood pressure, are abundant in salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseeds, and sunflower seeds are excellent providers of potassium and magnesium, two nutrients crucial for controlling blood pressure.
Allicin, a chemical found in garlic, is recognized for decreasing blood pressure.
Avocados: Packed with potassium, avocados support healthy fluid balance and blood pressure regulation.
Low-Fat Dairy: Low-fat cheese, skim milk, and Greek yogurt all offer calcium and protein without a lot of saturated fat.
Pomegranates: Due to the large amount of antioxidants in pomegranate juice, it has been shown to lower blood pressure.
Monounsaturated fatty acid-rich olive oil promotes heart health and may help decrease blood pressure.
Dark chocolate: Consuming dark chocolate with a high cocoa content (70 percent or more) in moderation has been associated with lowering blood pressure.
High blood pressure foods to avoid:
Controlling high blood pressure requires limiting or avoiding certain foods that can raise blood pressure. Avoid doing the following:
Foods heavy in sodium can lead to water retention and elevated blood pressure. Examples of such foods are processed meats, canned soups, and salty snacks.
Processed and packaged foods: These usually contain excessive salt levels, preservatives, and additives that might negatively affect blood pressure.
Fast Food and Takeout: These options are typically high in sodium, unhealthy fats, and excessive calories, all of which can worsen blood pressure.
Frozen Dinners and Convenience Meals: These are often loaded with sodium, even in seemingly small portions.
Canned Vegetables and Soups: While convenient, many canned products contain added sodium for preservation.
Cured Meats and Deli Cold Cuts: Bacon, sausage, ham, and other processed meats are usually high in sodium.
Excessive Dairy: Some dairy products, like certain cheeses, can be high in sodium. Opt for low-sodium alternatives.
Pickles and Sauerkraut: These are fermented and preserved with salt, making them sodium-rich.
Soy Sauce and Condiments: These can be very high in sodium. Opt for low-sodium or reduced-sodium versions.
High-Sodium Condiments: This includes ketchup, barbecue sauce, and salad dressings. Check labels for lower-sodium options.
Canned Beans and Legumes: Rinse thoroughly before use to reduce sodium content.
Baked Goods and Snack Foods: Items like pretzels, crackers, and chips often contain added sodium.
Certain Beverages: Some sports drinks, canned iced tea, and certain types of bottled water can be surprisingly high in sodium.
Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure. Limit your intake or opt for heart-healthy alternatives like red wine in moderation.
Avoiding these high-sodium and processed foods can contribute significantly to better blood pressure management. Remember to read labels, choose fresh, whole foods, and prioritize home-cooked meals to have better control over your sodium intake.
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For A Week:
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For DAY 1:
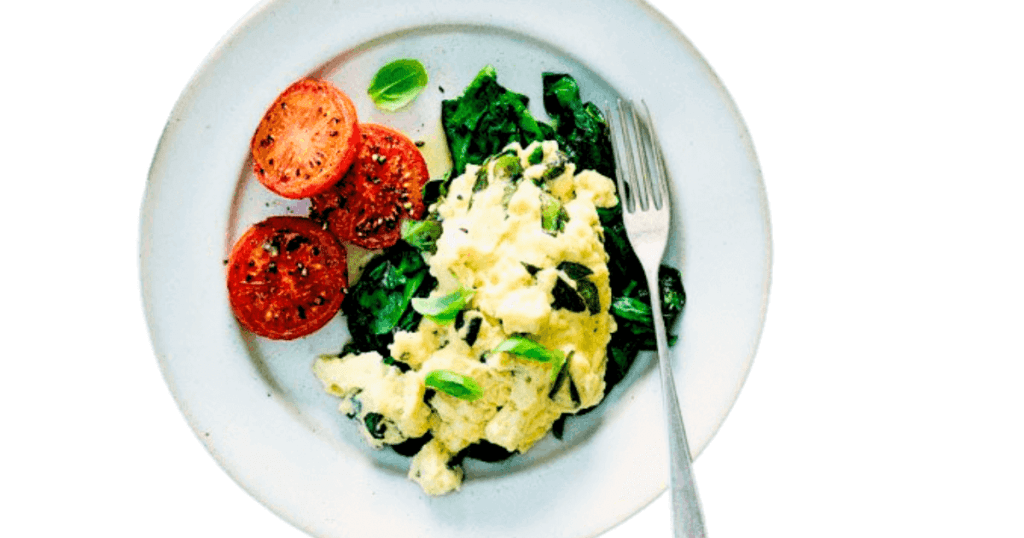

Breakfast:
- scrambled eggs with tomatoes and spinach.
- Whole grain bread.
- salad of fresh fruit.
Pre-Lunch:
Greek yogurt with sliced almonds and chia seeds on top.
Lunch:
- Chicken breast that has been grilled with mixed greens, cucumber, and avocado.
- Lemon vinaigrette with quinoa salad.
Afternoon Snacks:
- Hummus and carrot and cucumber sticks for dinner.
- Fish baked in a lemon-dill sauce.
- Brown rice and steamed broccoli.
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For DAY 2:

Breakfast
- Banana slices and cinnamon sprinkled on top of the oatmeal
- Green tea
Pre-Lunch:
An unsalted handful of mixed nuts
Lunch:
Mixed greens on the side and a splash of balsamic dressing with the lentil soup.
Evening Candies:
Pear slices with some almond butter on top.
Dinner:
Quinoa-based stir-fry of grilled vegetables and chickpeas.
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For DAY 3:
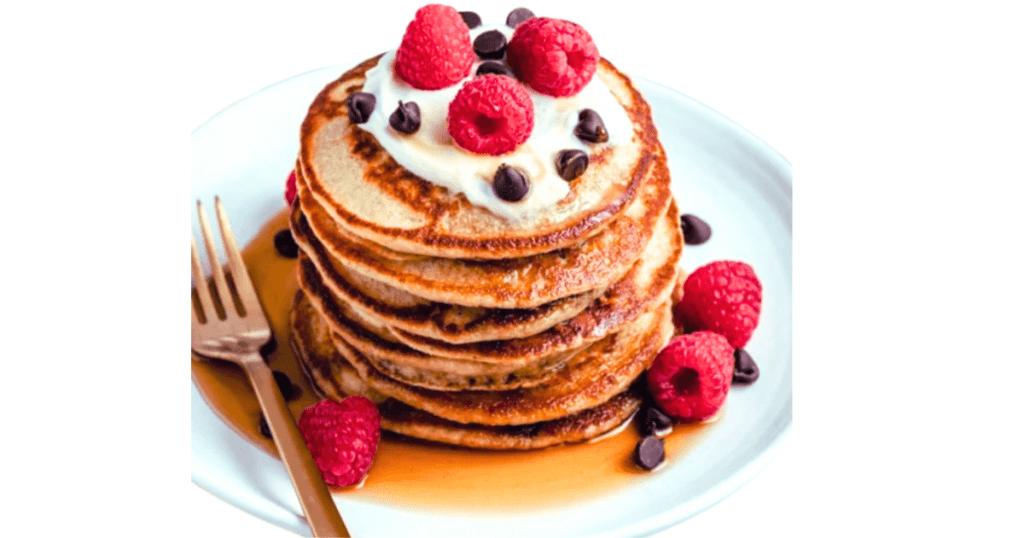

Breakfast:
Whole-grain pancakes with fresh berries and a dollop of Greek yogurt.
Pre-Lunch:
Celery sticks with peanut butter
Lunch:
Spinach and lentil salad with feta cheese and a lemon-tahini dressing.
Evening Snacks:
Air-popped popcorn with a sprinkle of nutritional yeast.
Dinner:
Baked chicken thighs with sweet potato and steamed green beans.
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For DAY 4:

Breakfast:
Spinach and feta omelette with a side of whole-grain toast
Pre-Lunch:
Cherry tomatoes with mozzarella and basil drizzled with balsamic reduction.
Lunch:
Quinoa-stuffed bell peppers with a side of mixed greens.
Evening Snacks:
Sliced cucumber with tzatziki sauce
Dinner:
Grilled shrimp skewers with a Mediterranean couscous salad
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For DAY 5:

Breakfast:
Granola-topped Greek yogurt parfait with mixed fruit
Pre-Lunch:
sliced apples with a dash of cinnamon.
Lunch:
Brown rice and a stir-fry of vegetables and tofu.
Afternoon Snacks:
Steamed edamame beans
Dinner:
Quinoa and baked cod with tomato and olive salsa
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For DAY 6:
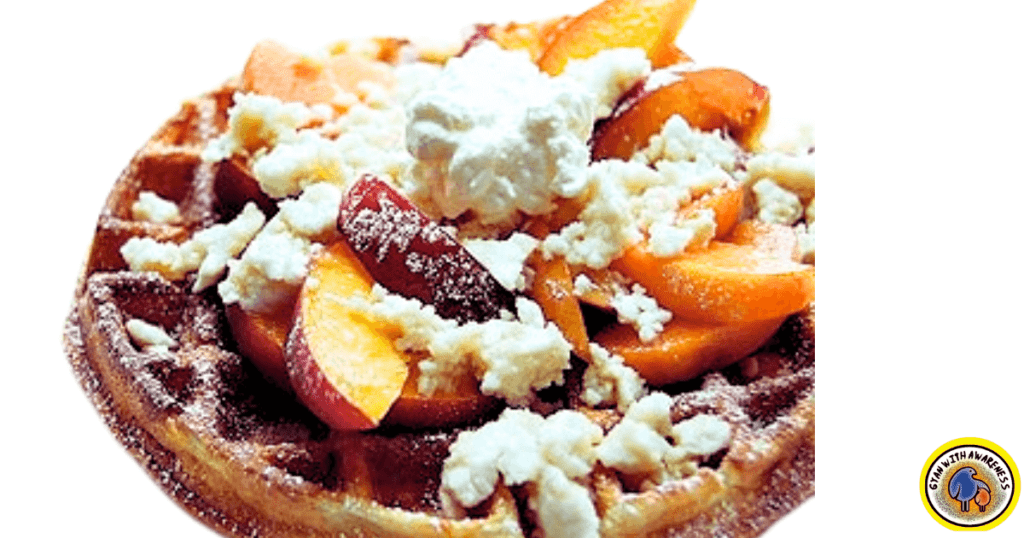

Breakfast:
Whole-grain waffles with sliced peaches and a dollop of ricotta cheese.
Pre-Lunch:
Avocado toast with a sprinkle of chili flakes.
Lunch:
Minestrone with a side of mixed greens and a drizzle of olive oil.
Evening Snacks:
Sliced bell peppers with guacamole
Dinner:
Grilled turkey burger with a side of sweet potato wedges and steamed broccoli.
High Blood Pressure Diet Menu For DAY 7:
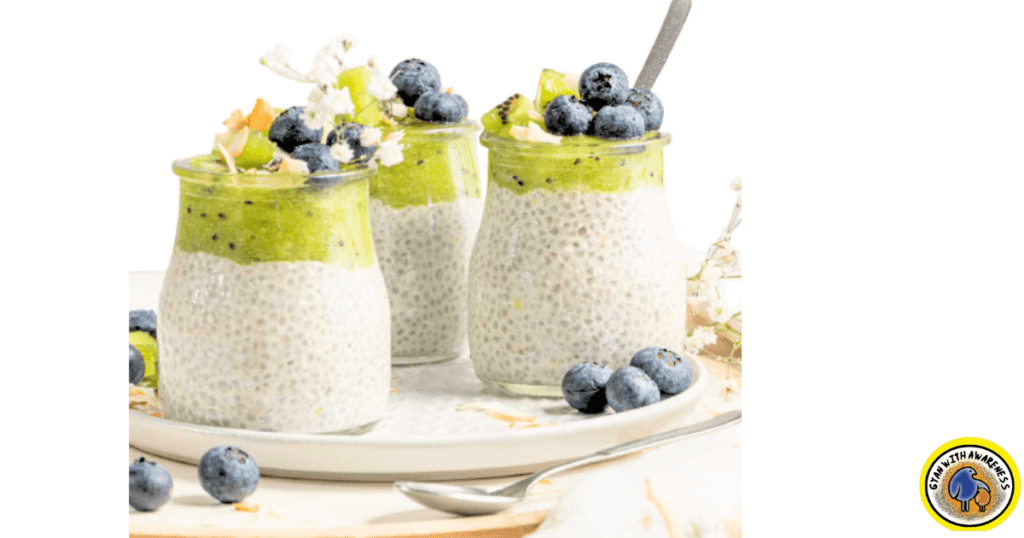

Breakfast:
Chia seed pudding topped with sliced almonds and kiwi.
Pre-Lunch:
Almond and date energy bites
Lunch:
Salmon and avocado salad with a citrus vinaigrette
Evening Snacks:
Mixed berry smoothie (made with unsweetened almond milk)
Dinner:
Roasted vegetable and quinoa stuffed bell peppers.
In conclusion, the High Blood Pressure Diet Menu plays a pivotal role in managing and mitigating the risks associated with hypertension. This carefully curated meal plan emphasizes nutrient-dense, whole foods that are rich in potassium, magnesium, and fibre while limiting sodium intake. By adhering to this diet, individuals can experience a range of benefits, including reduced blood pressure levels, improved cardiovascular health, and enhanced overall well-being.
Moreover, the High Blood Pressure Diet Menu serves as a versatile tool in preventing complications related to high blood pressure, such as heart disease and stroke. High Blood Pressure Diet Menu, emphasis on lean proteins, whole grains, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables promotes a balanced intake of essential nutrients crucial for optimal bodily function.
This diet also encourages a mindful and sustainable approach to eating, fostering a positive relationship with food. By making informed dietary choices, individuals can take an active role in their health and well-being. It is important to note that while the High Blood Pressure Diet Menu is an effective component of hypertension management, it should be complemented with regular exercise, stress management, and regular medical check-ups for a comprehensive approach to health.
Ultimately, the High Blood Pressure Diet Menu empowers individuals to take charge of their health and make choices that support their cardiovascular well-being, ensuring a higher quality of life and a brighter, healthier future.