A dislocated knee is a medical condition where the bones forming the knee joint are displaced from their normal positions. While not as common as other joint dislocations, a dislocated knee requires prompt medical attention due to the potential for severe complications. In this article, we’ll delve into the anatomy of the knee, causes of dislocation, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, first aid measures, medical treatment, and the importance of prevention and rehabilitation.
Knee Anatomy
Understanding the complexities of the knee’s structure is crucial to understanding a dislocated knee. The bones, ligaments, and tendons that make up the knee joint function together. Tendons join muscles to bones, guaranteeing appropriate function, while ligaments offer stability.
Also Read: Eyesight! Expert Tips for Enhancing and 8 Healthy Food
Improve Eyesight Naturally by Best 4 Boosting Tips
Best 7 Diabetic Foot Care And Cure Tips
11 Must-Try Diabetic Foot Care Exercises for Healthy Feet
Dislocated Knee:
This occurs most often as a result of a traumatic injury and causes a violent dislocation of the femur and tibia, the bones that comprise the knee joint. This displacement throws the joint’s natural alignment off, resulting in severe discomfort, edema, and a restricted range of motion. Neighboring ligaments and tissues may also be injured during this incident. Seeking prompt medical assistance is crucial to treating any concomitant injuries, reducing discomfort, and straightening the joint. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are often essential for the knee to restore its strength and functionality. It’s critical to receive thorough medical care right away because delays can lead to long-term issues including instability and arthritis.
What is a Dislocated Knee?
A dislocated knee occurs when the bones forming the knee joint, namely the femur and tibia, are forcefully displaced, usually due to a traumatic injury. This displacement results in severe pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Prompt medical attention is essential to realign the joint and address potential ligament and structural damage.
Types of Knee Dislocation:
Knee Dislocation Anterior:
It happens when the femur is violently forced in front of the tibia.
frequently linked to injuries caused by hyperextension.
Dislocation of the posterior knee:
It involves the tibia moving away from the femur and backward.
frequently brought on by powerful forces, such as a vehicle accident.
Knee Dislocation Lateral:
The tibia moves out from the femur and to the side.
may come from a twisting action or a direct hit.
Dislocation of the medial knee:
The tibia displaces itself by moving in the direction of the opposing leg.
usually results from an intense force applied to the outside knee.
Role of Knee pads:
Knee pads, a fundamental piece of protective gear, play a pivotal role in safeguarding our knees during various activities. Whether engaging in sports, working in construction, or pursuing recreational activities like skateboarding, knee pads provide an essential layer of defense against impacts and abrasions. These protective accessories are designed with durable materials and strategic padding to absorb shock and reduce the risk of injury. In this article, we delve into the world of knee pads, exploring their diverse uses, the technology behind their construction, and the indispensable protection they offer in preventing knee-related injuries across a spectrum of physical pursuits.
Benefits of Knee pads:
Impact Retention:
Knee pads lower the chance of injury when participating in sports, skating, or riding by distributing and absorbing impact forces.
Combined Defense:
In particular, they are essential in preventing fractures or contusions because they act as a layer of cushioning over the knee joint, minimizing direct stress on the patella and surrounding structures.
Resistance to Abrasion:
Knee pads protect from abrasions and scrapes, shielding the skin from harm and friction during activities involving contact with uneven terrain or surfaces like concrete.
Increased Stability
Knee caps give the knee joint more stability, which is advantageous for people who have had knee problems in the past or are healing from accidents. This additional support helps to stop lateral movements or hyperextension.
Comfort and Joint Warmth:
They offer a comfortable layer of padding and can help maintain joint warmth, which is particularly useful in colder conditions or during activities where muscles and joints need extra support.
Versatility:
Knee pads come in various styles and are adaptable to different activities, including sports, construction work, gardening, or any task that involves kneeling or potential impact to the knees.
Injury Prevention:
Wearing knee pads is a proactive measure to prevent injuries, making them essential for individuals participating in high-impact sports, recreational activities, or professions that involve kneeling or prolonged periods on the knees.
Best Top10 Knee Cap:
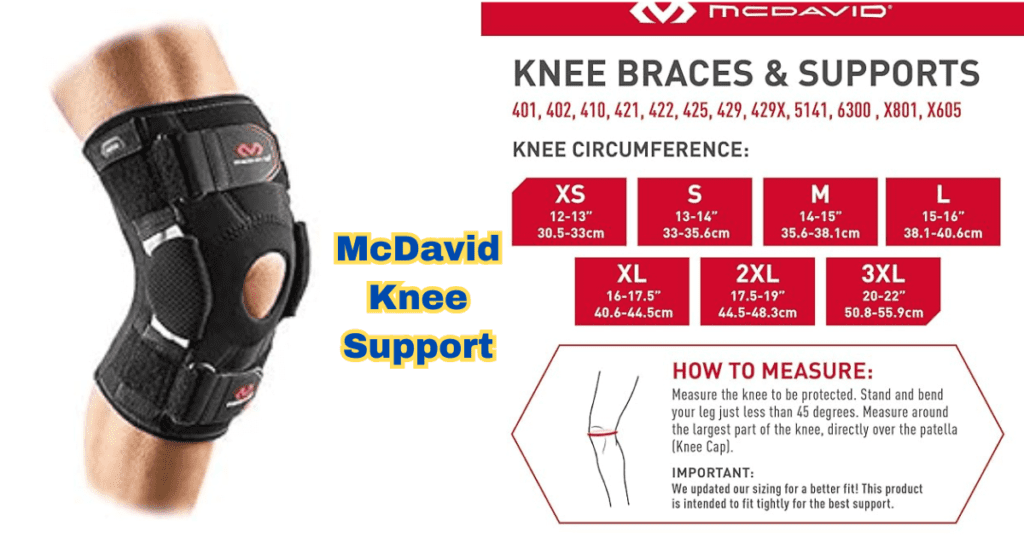
McDavid Knee Support
Quality Material: Neoprene blend for durability and flexibility.
Adjustability: Customizable straps for a secure and personalized fit.
Compression: Provides targeted compression support for the knee.
Breathability: Perforated design allows ventilation, reducing heat buildup.
Versatility: Suitable for various sports activities.
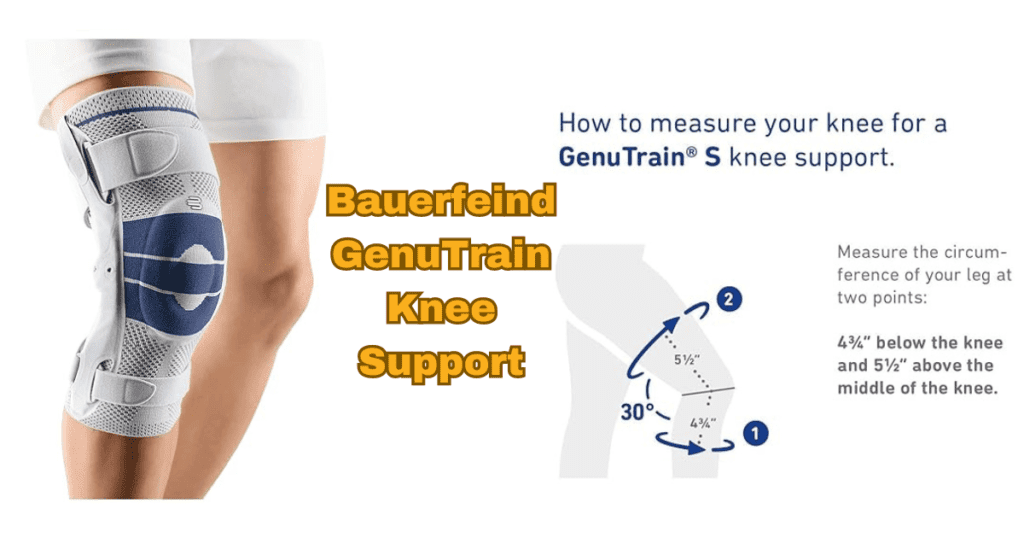
Bauerfeind GenuTrain Knee Support
Medical Grade Support: Offers medical-grade compression for stability.
Anatomical Fit: The contoured design ensures optimal support and comfort.
Durability: High-quality materials for long-lasting use.
Pain Relief: Eases discomfort associated with knee issues.
Brand Reputation: Well-known for orthopedic support products.
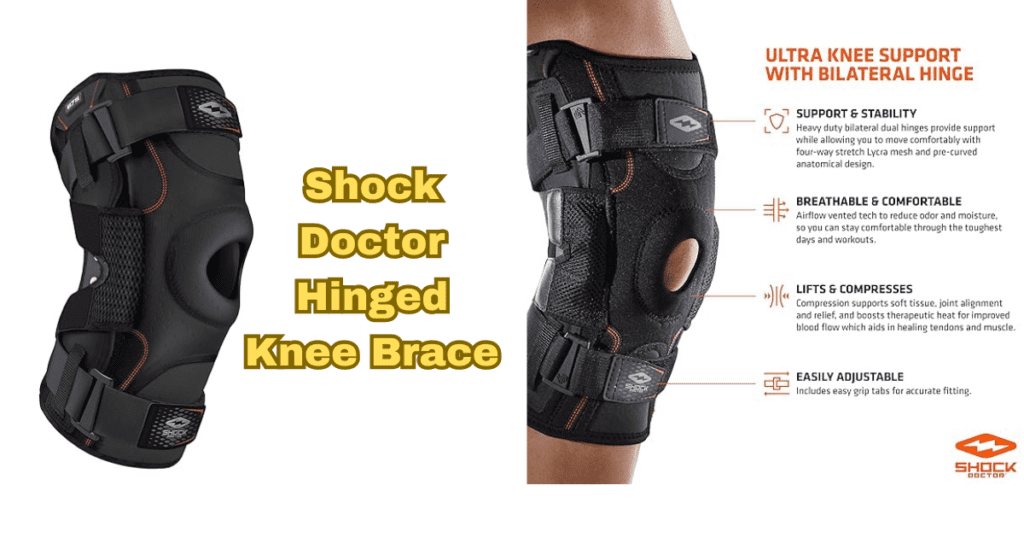
Shock Doctor Hinged Knee Brace
Designated specifically for patellar stability is patella stabilization.
Gel Cushioning: The comfort and support of gel inserts are increased.
Antimicrobial Fabric: Promotes cleanliness by combating bacteria and odor.
Securing a Secure Fit is ensured with the adjustable straps.
Adaptable Use: Fits a range of knee ailments.
Nike Pro Combat Knee Sleeve
Athletic Design: Blends performance with a sleek and stylish design.
Dri-FIT Technology: Moisture-wicking fabric for enhanced comfort.
Joint Support: Provides support without restricting movement.
Elasticity: Stretchable material for a snug fit.
Reputation: Trusted brand in sports apparel.

DonJoy Tru-Pull Lite Knee Brace
Dual Strapping: Dual straps allow for customizable compression.
ROM Support: Assists in maintaining a healthy range of motion.
Lightweight: Designed to be lightweight for comfortable wear.
Durable Construction: Built to withstand rigorous activities.
Orthopedic Expertise: Backed by orthopedic expertise.

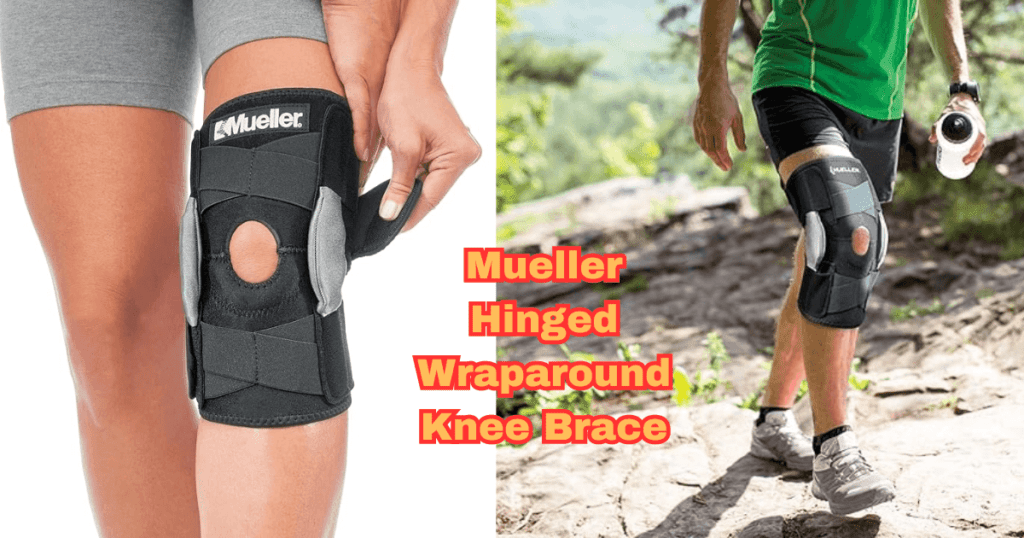
Mueller Hinged Wraparound Knee Brace
Maximum Support: Engineered for maximum patellar and knee support.
Adjustable: Straps for a personalized and secure fit.
Neoprene Material: Neoprene blend for durability and flexibility.
Open Patella Design: Allows proper alignment and movement.
Affordability: Budget-friendly option without compromising quality.
Pro-Tec Gel-Force Knee Sleeve
Gel Support: The gel pad provides targeted support to the knee.
Compression: Compression technology aids in recovery.
Comfortable Fit: Breathable and comfortable for extended wear.
Multi-Sport Use: Suitable for various sports and activities.
Ease of Use: Easy to put on and take off.

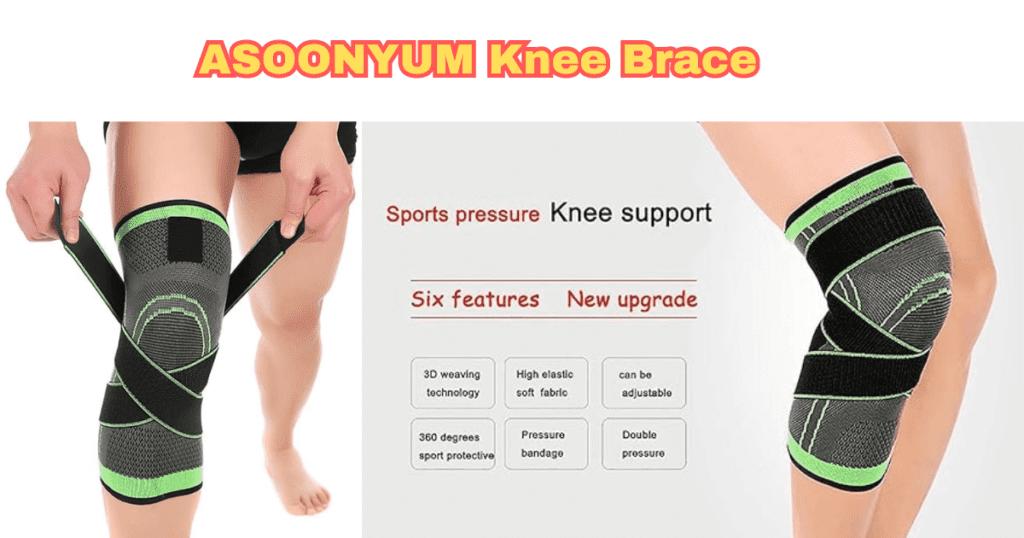
ASOONYUM Knee Brace
Silicone Pad: Silicone pad for enhanced patellar support.
Adjustable Straps: Straps for a customized and secure fit.
Anti-Slip Design: Prevents slipping during movement.
Breathable Fabric: Perforated fabric for ventilation.
Value for Money: Affordable option with quality features.
UFlex Athletics Knee Compression Sleeve
Open Patella Design: Allows for unrestricted patellar movement.
Compression Technology: Promotes blood circulation and recovery.
Antimicrobial Fabric: Prevents odor and bacterial growth.
Versatility: Suitable for a range of knee conditions.
Customer Ratings: Positive reviews for effectiveness.

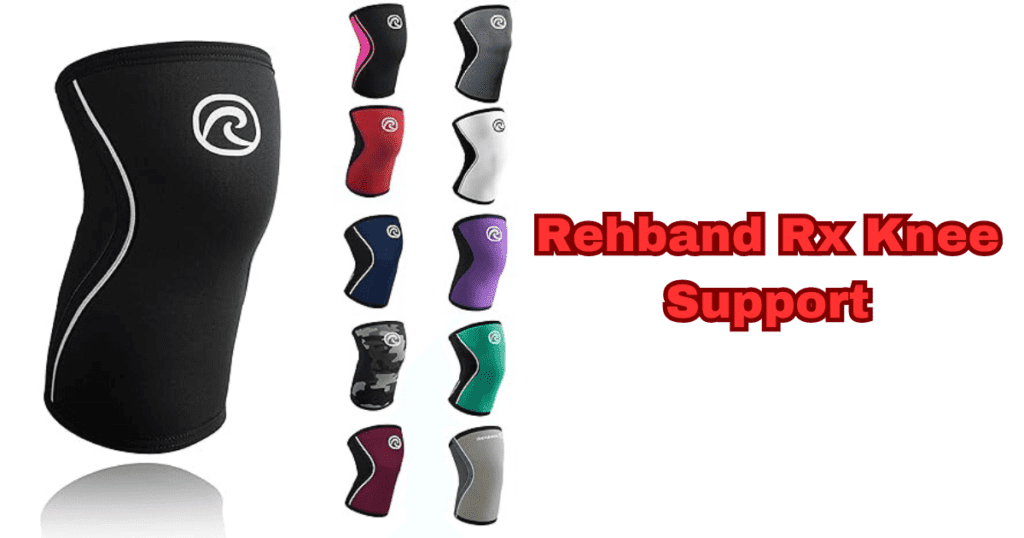
Rehband Rx Knee Support
Neoprene Support: Neoprene construction for stability.
Elasticity: Provides flexibility without compromising support.
Medical-Grade Quality: Trusted for medical and sports applications.
Anatomical Fit: Contoured design for a natural fit.
Clinically Proven: Backed by clinical studies for efficacy.

Difference Between Patella Dislocation and a Knee Dislocation:
Two different orthopedic problems affect the knee joint: a patella dislocation and a knee dislocation. The displacement of the kneecap from its natural position within the patellofemoral groove is specifically referred to as patella dislocation. This displacement is frequently brought on by abrupt direction changes, strikes directly, or strong knee twists. Severe discomfort, edema, and a noticeable patellar misalignment are the initial signs.
On the other hand, a knee dislocation involves the displacement of the entire knee joint, where the femur and tibia lose their normal alignment. This severe condition is usually a result of high-impact trauma, such as car accidents or sports injuries. The symptoms are more extensive, including severe pain, swelling, and significant limitations in knee mobility. Knee dislocations can potentially damage ligaments, blood vessels, and nerves surrounding the knee. Emergency medical intervention is crucial for realigning the joint, and subsequent rehabilitation, often involving surgical interventions, is essential for recovery.
Causes of Dislocated Knee:
Dislocated knees often result from traumatic incidents, such as high-impact collisions or awkward landings during sports activities. Athletes, especially those involved in contact sports, are prone to experiencing dislocations due to the nature of their physical engagement.
Symptoms and Indications
The major indicators of a dislocated knee include severe discomfort, swelling, and an obvious deformity of the knee joint. Another typical symptom is a limited range of motion, which makes it difficult to walk or bear weight.
Effect of Dislocated Knee:
Pain and Inflammation:
A dislocated knee frequently causes excruciating pain right away, which is frequently followed by noticeable swelling in the area surrounding the joint.
Limited Movement:
The displacement impairs the knee’s natural range of motion, which makes it difficult to bend or straighten and results in decreased mobility.
Damage to Soft Tissue:
The dislocation may cause tearing or stretching of the tendons, ligaments, and other soft structures surrounding the knee, which exacerbates instability.
Risk of Vascular and Nerve Injury:
Severe cases may damage blood vessels and nerves in the vicinity of the knee, posing risks of complications and requiring prompt medical attention.
Long-Term Instability:
Even after the dislocation is addressed, long-term instability can persist, making the knee more susceptible to future injuries.
Arthritis Risk:
Dislocated knees may increase the likelihood of developing arthritis over time, affecting joint function and causing chronic pain.
Rehabilitation Challenges:
Recovery often involves extensive rehabilitation and physical therapy to regain strength, stability, and functionality of the knee.
Psychological Impact:
The experience of a dislocated knee can have psychological effects, including fear of re-injury, anxiety, and emotional stress related to the traumatic event.
Diagnosis
Medical professionals diagnose a dislocated knee through a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. X-rays and MRIs help determine the extent of the dislocation and any associated damage to surrounding tissues.
Immediate First Aid
It’s crucial not to attempt to pop the knee back into place without professional assistance. Immediate first aid involves immobilization and elevation to minimize swelling and prevent further injury.
Medical Treatment
Once at a medical facility, a reduction procedure is performed to maneuver the knee joint back into place. Following the reduction, a comprehensive rehabilitation process is initiated to restore strength and mobility.
Complications
Long-term complications may arise from a dislocated knee, including arthritis and an increased risk of recurrent dislocations. Understanding these potential complications is vital for effective post-dislocation management.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing knee dislocations involves strengthening exercises to stabilize the joint and the use of protective gear, especially in sports where the risk of injury is higher.
Recovery Timeline
Patients can expect a gradual recovery process, including short-term limitations and a long-term rehabilitation plan tailored to their specific situation.
Patient Testimonials
Real-life experiences of individuals who have undergone a dislocated knee provide valuable insights into the challenges faced and the journey to recovery. Learning from others’ experiences can be both informative and reassuring.
Impact on Daily Life
The impact of a dislocated knee on daily life can be profound. Understanding the challenges and implementing effective coping mechanisms is crucial for a smoother recovery.
Get Back to Your Exercise
Reintroducing physical activity gradually after a dislocation necessitates close observation and commitment to a personalized rehabilitation regimen. Hurrying the procedure can result in difficulties and setbacks.
Expert Opinions
Orthopedic specialists provide their insights, offering tips for preventing knee dislocations and maintaining overall joint health.
Dislocated Knee Cap vs. Knee Pads: A Comparative Overview:
Nature of Injury:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Involves the displacement of the patella (knee cap) from its normal position, often due to trauma.
Knee Pads: Designed for preventive protection, offering cushioning and support during various activities.
Causes:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Primarily caused by traumatic incidents or high-impact accidents.
Knee Pads: Used as a proactive measure to prevent injuries during activities prone to knee impact.
Function:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Requires immediate medical attention for diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation.
Knee Pads: Act as a proactive shield, minimizing the risk of injuries by absorbing shocks and distributing impact.
Usage:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Relevant post-injury, necessitating medical intervention.
Knee Pads: Worn during various activities like sports, construction work, or recreational pursuits to prevent injuries.
Protection Level:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Involves potential ligament and cartilage damage, requiring comprehensive medical assessment.
Knee Pads: Offer protection against superficial injuries, reducing the severity of impacts.
Material:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Involves the body’s natural anatomy, ligaments, and tendons.
Knee Pads: Constructed with durable materials, often including foam or gel padding for impact absorption.
Medical Attention:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Demands immediate attention from healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Knee Pads: Designed for preventive use, reducing the need for immediate medical intervention.
Recovery:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Involves a rehabilitation process guided by medical experts, with varied recovery times.
Knee Pads: Focus on preventing injuries, and minimizing downtime associated with recovery.
Cost:
Dislocated Knee Cap: Medical expenses may include diagnostic tests, consultations, and potential surgery, impacting overall cost.
Knee Pads: A relatively affordable investment compared to potential medical costs associated with knee injuries.
Preventive actions:
Restricted preventive strategies; post-injury care is the main focus for dislocated knee caps.
Knee pads: a proactive measure that provides a practical way to lessen the risk of knee injury during a variety of activities.
Top 10 Home Care Tips for Dislocated Knee:
Certainly, while immediate medical attention is crucial for a dislocated knee, here are some general tips that may provide initial relief at home. It’s important to note that these tips are not a substitute for professional medical advice, and consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Immobilize the Knee:
Keep the knee in a stable position and avoid putting weight on it.
Apply Ice Packs:
Use ice packs to reduce swelling. Apply for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours.
Elevate the Leg:
Elevate the leg to help minimize swelling. Place a pillow under the knee.
Compression Bandage:
Use a compression bandage to provide support and control swelling.
Over-the-Counter Pain Medications:
Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen may help manage pain and inflammation.
Rest:
Allow the knee to rest and avoid strenuous activities.
Avoid Self-Adjustment Attempts:
Do not try to pop the knee back into place at home. Seek professional help
Exercises for Mild Range of Motion:
As directed by a healthcare provider, engage in mild, regulated range-of-motion exercises.
Drinking enough water and eating right:
To help the body repair itself, drink plenty of water and eat a healthy diet.
Speak with a Medical Expert:
For a comprehensive assessment and a suitable treatment plan, get medical help right now.
In conclusion, a dislocated knee is a serious injury that demands immediate attention and proper care. From understanding the anatomy of the knee to implementing prevention strategies and navigating the recovery journey, each step is crucial. Seeking professional guidance and following a comprehensive rehabilitation plan are key to a successful recovery.
FAQ:
How long does it take to recover from a dislocated knee?
Recovery timelines vary but generally involve weeks to months of rehabilitation.
Can a dislocated knee lead to long-term complications?
Yes, potential complications include arthritis and an increased risk of recurrent dislocations.
Are dislocated knees common in sports?
Athletes, especially those in contact sports, are more susceptible to dislocated knees.
Is it possible to self-treat a dislocated knee at home?
No, it is not advised to try popping the knee back on your own without medical help.
What safeguards can be put in place to stop knee dislocations?
Knee dislocations can be avoided with the use of protective equipment and strengthening activities.
Also Read: Eyesight! Expert Tips for Enhancing and 8 Healthy Food
Improve Eyesight Naturally by Best 4 Boosting Tips
Best 7 Diabetic Foot Care And Cure Tips