Diabetes Blood Sugar Chart and 20 Effective Ways are right away, controlling blood sugar levels is essential for people with diabetes to keep their health at its best. The Blood Sugar Chart serves as a crucial compass in navigating one’s health journey. It unveils the intricate dance of glucose levels within our bodies, offering insights into our well-being. By illustrating the fluctuations of blood sugar, this chart empowers us to grasp the impact of diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices.
The blood Sugar Chart is a cornerstone in diabetes management, aiding in informed decisions and promoting a proactive approach. Recognizing the significance of maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, a Blood Sugar chart encourages a partnership between individuals and their health, fostering a path toward better control, reduced risks, and enhanced quality of life.

Sometimes, to lower high blood sugar levels, quick action may be required. In this manual, we’ll look at practical methods for quickly lowering blood sugar.
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can occur due to various factors such as consuming high-carbohydrate foods, missed medication doses, or insufficient insulin production. It’s important to elevated blood sugar levels promptly to prevent complications and promote overall well-being.
The methods discussed in this guide focus on natural and practical approaches to lower blood sugar quickly. These strategies include dietary modifications, physical activity, hydration, and mindful lifestyle choices. By implementing these techniques, individuals can help stabilize their blood sugar levels and feel better in a short period. It’s crucial to remember that lowering blood sugar right away is just the beginning.
By understanding how to lower blood sugar straight away and incorporating these tactics throughout daily life, people can actively strive toward better blood sugar control and improved general health. For particular guidance tailored to your needs, don’t forget to consult with a healthcare professional.
Read More: Dangerous Complications: Decoding 8 Health Risks Linked to Diabetes
100% Best Way to Lower Blood Sugar Levels Naturally
Blood Sugar Chart:
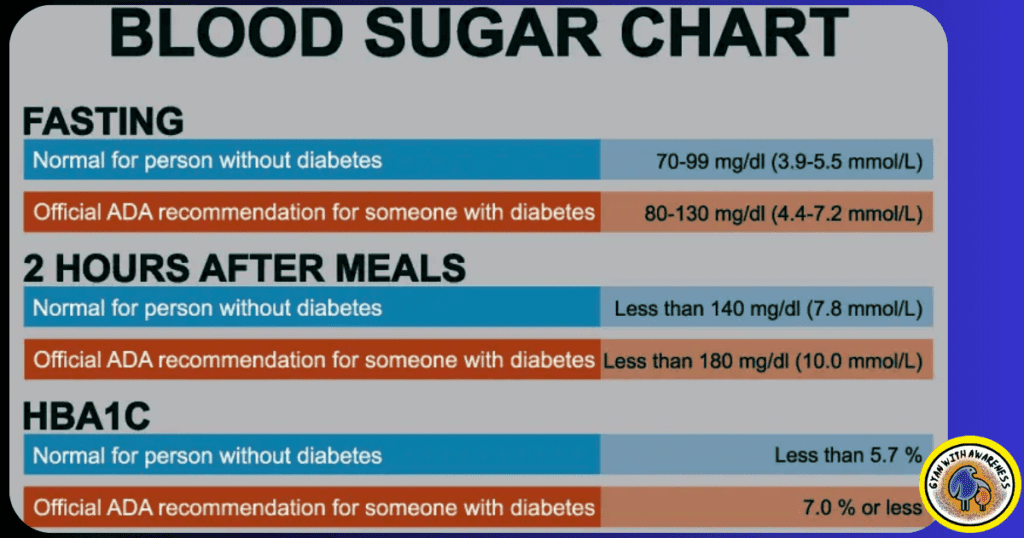
Normal Blood Sugar Levels For all Age Groups (Children, Adults, Seniors)
Children (Fasting Blood Sugar Chart):
Infants: Generally, 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.6 mmol/L).
Children (2-6 years): Around 80-110 mg/dL (4.4-6.1 mmol/L).
Children (7-12 years): Similar to adults, typically 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.6 mmol/L).
Adults (Fasting Blood Sugar Chart):
Normal Range: Usually 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.6 mmol/L).
Prediabetes: Fasting levels between 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L).
Diabetes: Fasting levels consistently at or above 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L).
Seniors (Fasting Blood Sugar chart):
For older adults, the same range of 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.6 mmol/L) is considered normal.
The risk of prediabetes and diabetes increases with age, so regular monitoring is important.
Postprandial (After Eating) Blood Sugar chart:
For adults, levels are generally considered normal if they stay below 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after a meal.
For seniors, the target might be slightly higher, around 160 mg/dL (8.9 mmol/L).
Keep in mind that there may be individual differences, and you should always speak with a healthcare provider before interpreting and managing your blood sugar levels. All age groups must maintain good blood sugar levels, which require regular monitoring, a balanced diet, physical activity, and checkups.
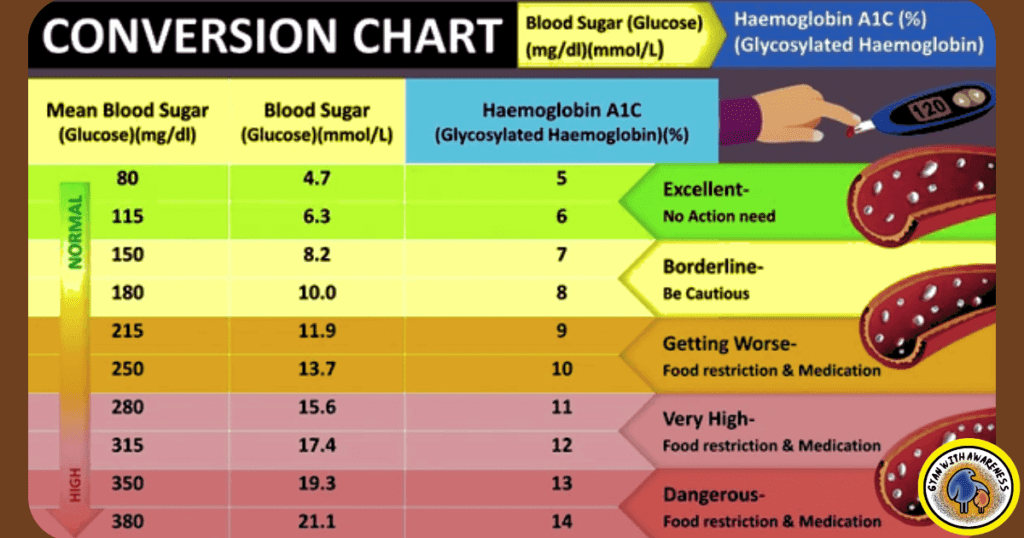
A Blood Sugar Chart is essential for tracking and managing glucose levels effectively. It provides a visual representation of how diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle choices impact blood sugar levels over time. Blood Sugar Chart is a tool that enables individuals, especially those with diabetes, to recognize patterns, identify potential fluctuations, and make informed decisions to maintain stable levels. The Blood Sugar Chart serves as a communication bridge between individuals and healthcare professionals, aiding in personalized treatment adjustments. By promoting proactive monitoring, early intervention, and informed self-care, a Blood Sugar Chart empowers individuals to take control of their health, prevent complications, and lead a healthier life.
Fasting & Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels Chart:
Fasting and non-fasting blood sugar levels are two key measurements that offer insights into an individual’s glucose metabolism and overall health. Here we are providing a Blood Sugar Chart for awareness for all.
Fasting Blood Sugar Chart:
Fasting blood sugar refers to the amount of glucose present in the bloodstream after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. This measurement is typically taken in the morning before consuming any food or beverages. Normal fasting blood sugar levels typically fall within the range of 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.6 mmol/L). Levels higher than this might indicate prediabetes or diabetes. Fasting blood sugar is often used as a baseline assessment and can help diagnose diabetes or assess the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies.
Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Chart:
Non-fasting blood sugar levels are taken at various times during the day, usually after meals. These measurements or Blood Sugar Charts provide valuable information about how the body responds to dietary intake and can help gauge postprandial glucose spikes. After a meal, blood sugar levels naturally rise, but they should ideally return to baseline levels within a few hours. For adults, non-fasting levels should generally stay below 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating. Elevated postprandial levels can be indicative of impaired glucose tolerance and warrant attention.
Understanding both fasting and non-fasting blood sugar levels is crucial for effective diabetes management. Regular monitoring, coupled with a balanced diet, physical activity, and medical guidance, ensures that blood sugar levels are within a healthy range, reducing the risk of complications and promoting overall well-being.
How and When to Test Blood Sugar Levels:
Testing blood sugar is a critical aspect of managing conditions like diabetes and maintaining overall health. The process involves a few key steps to ensure accurate readings:
How to test Blood Sugar Levels:
Wash Hands:
Begin by washing your hands with warm water to ensure they are clean and free from any substances that could affect the reading.
Prepare the Testing Site:
Choose a fingertip, usually on the sides, and clean it with an alcohol swab. Allow it to dry completely before proceeding.
Prick the Finger:
Use a lancet device to prick the chosen fingertip gently. This minimizes discomfort while obtaining a small blood sample.
Collect Blood Samples:
Place the blood sample on the test strip or into the glucometer according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Most modern glucometers require a small drop of blood.
Read the Result:
The glucometer will analyze the blood sample and display the blood sugar reading on the screen.
When to Test Blood Sugar:
Fasting:
Fasting blood sugar levels are usually measured in the morning after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. This provides a baseline reading.
Pre-meal:
It’s helpful to test blood sugar before meals to understand how your levels respond to different foods.
Post-meal:
Testing 1-2 hours after a meal provides insight into how your body processes glucose after eating.
Random:
Occasionally testing at different times of the day helps identify trends and potential issues that might not be captured by routine measurements.
As Advised by the Healthcare Provider:
Your healthcare provider might recommend additional testing times, especially if you’re on medication, experiencing symptoms, or making changes to your diabetes management plan.
Regular monitoring helps you make informed decisions about diet, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. It’s important to record your results and share them with your healthcare provider during appointments. They can help interpret the readings and guide you toward maintaining optimal blood sugar levels for better overall health.
Diabetes Strategies to Lower Blood Sugar Levels Immediately:
It is important to note that reducing blood sugar immediately should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. However, here are some general tips that may help in managing blood sugar levels:
Keep Hydrated:
Drinking enough water can help hydrate you and flush out extra sugar from your bloodstream. Aim to consume 8 glasses of water or more each day.
Exercise:
By improving insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake by the muscles, exercise can help reduce blood sugar levels. Spend at least 30 minutes each day engaging in moderate-intensity exercises like walking, cycling, or swimming.
Consume meals high in fiber:
They assist in keeping your glucose levels steady by slowing the absorption of carbohydrates into the bloodstream. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and bean products in your diet.
Portion Size Control:
Portion control is important to prevent consuming too many carbohydrates, which can lead to blood sugar increases. Choose meals that are well-balanced and contain lean proteins, good fats, and complex carbohydrates.
Observe Your Carbohydrate Intake:
Track your daily carbohydrate intake and spread it out throughout the day. Avoid taking a lot of carbohydrates all at once because this can cause a sharp rise in blood sugar.
Reduce Stress:
Stress hormones can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Use stress-reduction strategies like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or relaxing activities to help you decompress.
Get Enough Sleep:
Sleep deprivation can impair insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation. For optimum health and blood sugar control, aim for 7-8 hours of good sleep each night.
Avoid Sugary Foods and Beverages:
Limit your consumption of sugary foods, desserts, sodas, and sugary beverages, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Consider Medication:
If blood sugar levels remain consistently high, despite lifestyle modifications, consult a healthcare professional who may prescribe appropriate medication to help manage blood sugar levels.
Regular Inspection:
A glucometer can be used to frequently check your blood sugar levels. This will enable you to make the necessary adjustments by better understanding how your body reacts to various diets, exercises, and medications.
To create a personalized plan that meets your unique needs, engage together with your healthcare team. Keep in mind that everyone’s response to these tactics may differ.
Keep Moving After Meals:
By improving insulin sensitivity and encouraging glucose uptake by the muscles, modest exercise, like a quick walk, can help reduce blood sugar levels after meals.
Limit Your Consumption of Refined Carbohydrates:
Foods manufactured with refined carbs, such as white rice, white bread, and sugary snacks, can quickly raise blood sugar levels. Choose alternatives made of whole grains, which are higher in fiber and slower to raise blood sugar.
Include Protein in Meals:
Meals, such as chicken, fish, tofu, or lentils, help slow down the absorption of carbohydrates and help manage your glucose levels.
Greater intake of fiber:
In addition to helping people feel fuller for longer, diets high in fiber also delay the bloodstream’s ability to absorb sugar. Oats, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and vegetables are excellent sources of soluble fiber.
Maintain Regular Meal Timings:
Eating regularly scheduled meals at regular intervals and spreading out meals evenly throughout the day can assist in maintaining steady blood sugar levels. Never skip meals or go longer than necessary without eating.
Keep an eye out for hidden sugars:
Be mindful of any hidden sugars in processed meals, sauces, and beverages. When possible, read food labels and choose low- or sugar-containing alternatives.

Think of organic vitamins AND supplements:
Magnesium, alpha-lipoic acid, and other organic minerals may help with glucose control and insulin sensitivity. However, before beginning any new supplements, speak with a medical expert.
Seek Support:
Joining a support group or seeking guidance from a diabetes educator or nutritionist can provide valuable information and motivation for managing blood sugar effectively.
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Alcohol can interfere with blood sugar regulation and cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation and avoid sugary mixed drinks.
Regularly Review Medications:
If you are taking medications to manage diabetes, it’s essential to regularly review them with your healthcare provider. They can assess the effectiveness of your current medications and make any necessary adjustments.
What to Do When Blood Sugar Is Too High or Low?
To effectively manage their disease, people with diabetes must understand the Blood Sugar Chart, and how to lower sugar levels quickly. If untreated, elevated levels can hurt health and may even cause difficulties. You can take immediate action to lower raised glucose levels by putting the techniques covered in this guide into practice, including changing your food, exercising, drinking plenty of water, and establishing mindful lifestyle habits.
By proactively addressing high blood sugar levels and maintaining a comprehensive diabetes management plan, you can lead a healthier and more fulfilling life with diabetes. Remember, knowledge is power, and taking control of your blood sugar levels is a vital aspect of effectively managing diabetes.
As a result, the Blood Sugar Chart emerges as a crucial ally on the path to optimum health, especially for people who are coping with illnesses like diabetes. A blood Sugar Chart or graph represents a dynamic narrative of one’s body’s reaction to numerous factors rather than merely being a list of data. People can get a comprehensive awareness of their particular physiological patterns and triggers by meticulously monitoring and analyzing their blood sugar measurements. With Blood Sugar Chart knowledge, they can adjust their everyday decisions to promote stable blood sugar levels, including diet and activity choices.
Ultimately, the Blood Sugar Chart embodies empowerment. It empowers individuals to advocate for their health, make informed decisions, and drive positive change. By harnessing the data it presents, individuals are equipped with a tool that transcends numbers, paving the way toward a life characterized by balance, vitality, and triumph over health challenges.
Also Read: Rosemary: Victory on Diabetes with 10 Remedies- Part 1
The Best Medicinal Plants Chart: 10 Medicinal Plants in India
FAQ:
What are the normal ranges for blood sugar?
Depending on the moment of the measurement and one’s health, there are different normal blood sugar ranges. Blood sugar readings taken after an overnight fast usually range from 70 to 100 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.6 mmol/L). Adults should ideally maintain postprandial levels under 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after a meal. Individual reactions, however, can differ. Fasting levels of 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) are frequently indicative of prediabetes, but diabetes is diagnosed when fasting levels are persistently at or above 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L). Blood sugar levels are kept within specified ranges with the help of regular monitoring and medical direction, which lowers the risk of problems and improves general health.
Is random blood sugar 180 normal?
A random blood sugar level of 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) is elevated and not considered within the normal range. Normal random blood sugar levels are typically below 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L). A reading of 180 mg/dL could indicate potential glucose dysregulation, such as impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes, and requires attention. While random blood sugar levels can vary due to recent food intake, stress, or other factors, consistently high readings should be discussed with a healthcare professional. It’s important to monitor and address blood sugar levels to prevent complications and maintain overall health, especially for individuals at risk of or diagnosed with diabetes.
What is the Blood Sugar Chart?
A Blood Sugar Chart is a visual tool that displays recorded blood sugar readings over a defined period. Blood Sugar Chart helps individuals, particularly those with diabetes, track their glucose levels and identify patterns and trends. The Blood Sugar Chart typically includes the time of day, date, and corresponding blood sugar values. By visually representing these data points, individuals can observe how various factors such as meals, exercise, and medications influence their blood sugar. Blood Sugar Chart empowers better self-management, aiding in making informed decisions about lifestyle adjustments and treatment strategies. Healthcare providers also use Blood Sugar Charts to assess the effectiveness of interventions and guide personalized care plans.



1 thought on “Blood Sugar Chart and 20 Effective Ways For Boosting Wellness”